Human Body Parts Names In English With Images | Human Body Diagram
Introduction
We’re excited to take you on a fascinating tour into the complex world of human body parts! For pupils, comprehending the amazing mechanics of our bodies is not only intriguing but also essential to gaining a comprehensive understanding of biology. Imagine being able to understand the complexities underlying each pulse, each breath, and each eyeblink. This website strives to serve as your comprehensive reference, presenting an in-depth examination of the amazing parts of the human body together with colorful pictures and diagrams. Join us as we set out on an illuminating journey to discover the wonders that make us who we are, whether you’re an inquisitive student or an aspirant medical professional.What Is the Human Body?
The complex human body, made up of cells, tissues, organs, and systems, functions in unison to sustain life. Understanding its components is important for healthcare and advantageous for everyone’s general well-being. Understanding human anatomy enables smart decisions for a healthy existence amid rising health awareness.Bones In the Human Body
The skeletal system is the basis of our physical existence. The human skeleton, which consists of 206 different bones, gives the body form, protects the organs, and allows for mobility. The sturdy femur and the delicate inner ear bones for hearing both play a crucial role in our everyday activities.A Glimpse of Human Body Parts Names With Images
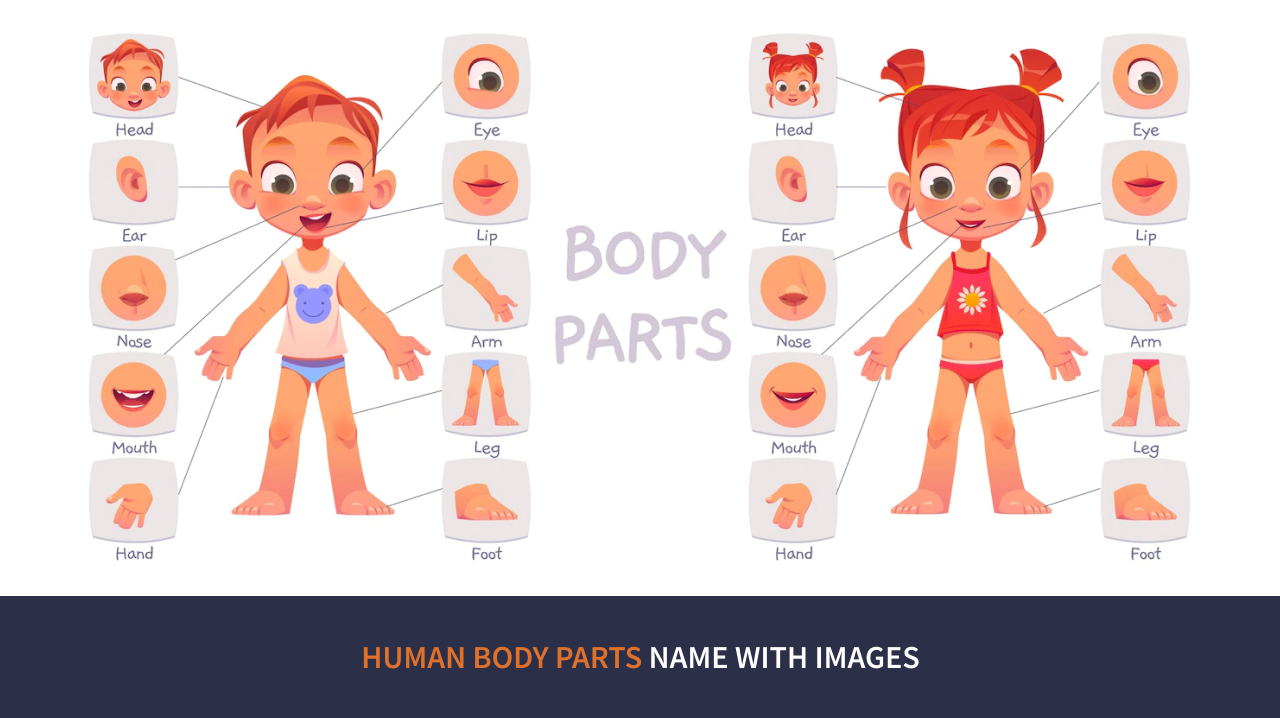
1. Head and Neck- Skull: The brain’s protective covering, which guards our most critical organs.
- Eyes: Our sense of vision helps us recognize colors, forms, and movement in the environment.
- Nose: The nose is the organ that gives us the ability to smell and flavor.
- Mouth: The place where digestion starts with the chewing motion and saliva production that prepares food for future digestion.
2. Chest and Abdomen
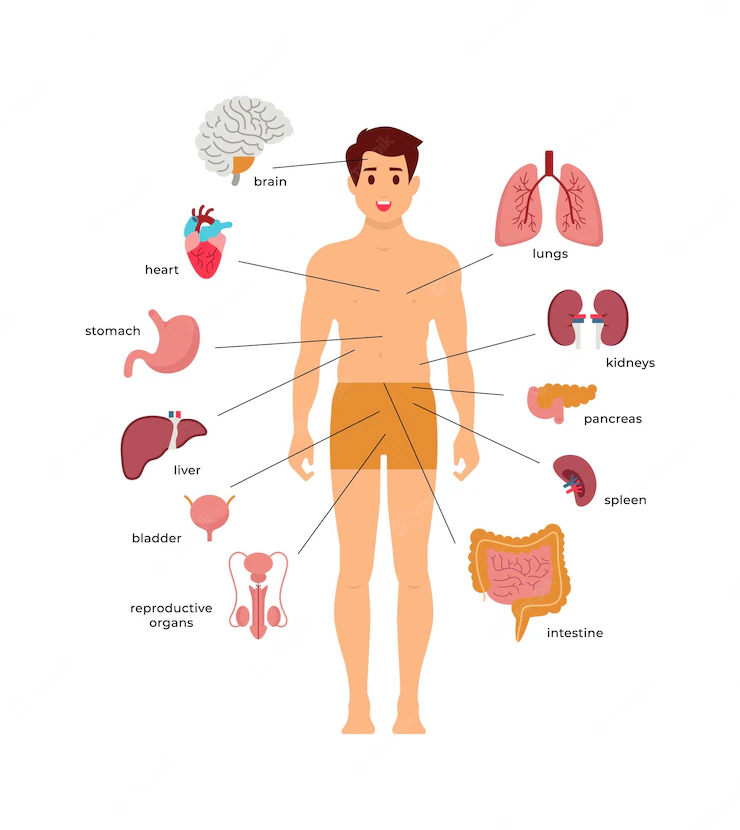
- Heart: The muscle pump that powers the circulatory system that distributes nutrients and oxygen throughout the body is the heart.
- Lungs: Essential organs that allow humans to breathe and maintain life by exchanging oxygen.
- Stomach: A muscular pouch where food digestion takes place, the stomach uses acid and enzymes to break down the meal.
- Liver: Performs vital metabolic and detoxifying tasks that are needed for preserving body equilibrium.
3. Arms and Hands
- Shoulders: The joints that link the arms to the body and enable a variety of arm motions.
- Biceps and Triceps: Muscles make the arms strong and flexible, making lifting and pushing easier.
- Hands: Dexterous tools with complex touch sensations that are useful for activities demanding fine control of movement and sensory awareness.
4. Pelvis and Legs
- Pelvis: A basin-shaped structure that connects the legs and supports the spine, distributing weight and ensuring stability.
- Hips: Ball-and-socket joints, which enable motions like walking, running, and leaping, are essential for lower body mobility.
- Thighs: Leg-movement and stability-supporting muscles in the thighs that help in standing and walking.
- Feet: Comprised of bones, muscles, and ligaments that support our body weight, feet are complex structures that provide movement and balance.
Human Body Diagram
Here is a simplified representation of the human body that shows the main body components and where they are situated. This figure is a helpful place to start when trying to understand how the many components of the human body are organized.
Conclusion
The human body is proof of the wonders of nature’s engineering. This extensive introduction to human body parts has given us a peek at the many different pieces that go into making us who we are. We may better enjoy the symphony of life that plays within us if we are aware of the names, functions, and relationships of different bodily components. Explore each category in further detail, and learn about the mechanics that underlie their operations. Remember that this information is a path to a better, more informed existence, whether you’re an aspirant healthcare professional, an inquisitive student, or just someone eager to comprehend the wonders of your own body.FAQs
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
The human body contains 78 organs.
Tendons connect muscles to bones, allowing muscles to contract and pull on bones to move the body.
The body can inhale oxygen and release waste gases thanks to the lung’s ability to exchange carbon dioxide and oxygen.
The skin acts as a barrier, controls body temperature, and contains sensory receptors that allow people to feel touch, pain, and temperature.